🔐 A curated list of awesome resources for LLMSecOps (Large Language Model Security Operations) 🧠
Architecture | Vulnerabilities | Tools | Defense | Threat Modeling | Jailbreaks | RAG Security | PoC's | Study Resources | Books | Blogs | Datasets for Testing | OPS Security | Frameworks | Best Practices | Research | Tutorials | Companies | Community Resources
LLM safety is a huge body of knowledge that is important and relevant to society today. The purpose of this Awesome list is to provide the community with the necessary knowledge on how to build an LLM development process - safe, as well as what threats may be encountered along the way. Everyone is welcome to contribute.
Important
This repository, unlike many existing repositories, emphasizes the practical implementation of security and does not provide a lot of references to arxiv in the description.
Overview of fundamental architectural risks and challenges in LLM systems.
| Risk | Description |
|---|---|
| Recursive Pollution | LLMs can produce incorrect output with high confidence. If such output is used in training data, it can cause future LLMs to be trained on polluted data, creating a feedback loop problem. |
| Data Debt | LLMs rely on massive datasets, often too large to thoroughly vet. This lack of transparency and control over data quality presents a significant risk. |
| Black Box Opacity | Many critical components of LLMs are hidden in a "black box" controlled by foundation model providers, making it difficult for users to manage and mitigate risks effectively. |
| Prompt Manipulation | Manipulating the input prompts can lead to unstable and unpredictable LLM behavior. This risk is similar to adversarial inputs in other ML systems. |
| Poison in the Data | Training data can be contaminated intentionally or unintentionally, leading to compromised model integrity. This is especially problematic given the size and scope of data used in LLMs. |
| Reproducibility Economics | The high cost of training LLMs limits reproducibility and independent verification, leading to a reliance on commercial entities and potentially unreviewed models. |
| Model Trustworthiness | The inherent stochastic nature of LLMs and their lack of true understanding can make their output unreliable. This raises questions about whether they should be trusted in critical applications. |
| Encoding Integrity | Data is often processed and re-represented in ways that can introduce bias and other issues. This is particularly challenging with LLMs due to their unsupervised learning nature. |
From Berryville Institute of Machine Learning (BIML) paper
Common vulnerabilities and security issues found in LLM applications.
| Vulnerability | Description |
|---|---|
| Hallucination and Misinformation | These vulnerabilities often manifest themselves in the generation of fabricated content or the spread of false information, which can have far-reaching consequences such as disseminating misleading content or malicious narratives. |
| Harmful Content Generation | This vulnerability involves the creation of harmful or malicious content, including violence, hate speech, or misinformation with malicious intent, posing a threat to individuals or communities. |
| Prompt Injection | Users manipulating input prompts to bypass content filters or override model instructions can lead to the generation of inappropriate or biased content, circumventing intended safeguards. |
| Robustness | The lack of robustness in model outputs makes them sensitive to small perturbations, resulting in inconsistent or unpredictable responses that may cause confusion or undesired behavior. |
| Output Formatting | When model outputs do not align with specified format requirements, responses can be poorly structured or misformatted, failing to comply with the desired output format. |
| Information Disclosure | This vulnerability occurs when the model inadvertently reveals sensitive or private data about individuals, organizations, or entities, posing significant privacy risks and ethical concerns. |
| Stereotypes and Discrimination | If model's outputs are perpetuating biases, stereotypes, or discriminatory content, it leads to harmful societal consequences, undermining efforts to promote fairness, diversity, and inclusion. |
Security scanning and vulnerability assessment tools for LLM applications.
| Tool | Description | Stars |
|---|---|---|
| 🔧 Garak | LLM vulnerability scanner |  |
| 🔧 ps-fuzz 2 | Make your GenAI Apps Safe & Secure 🚀 Test & harden your system prompt |  |
| 🗺️ LLMmap | Tool for mapping LLM vulnerabilities |  |
| 🛡️ Agentic Security | Security toolkit for AI agents |  |
| 🔒 LLM Confidentiality | Tool for ensuring confidentiality in LLMs |  |
| 🔒 PyRIT | The Python Risk Identification Tool for generative AI (PyRIT) is an open access automation framework to empower security professionals and machine learning engineers to proactively find risks in their generative AI systems. |  |
| 🔧 promptfoo | LLM red teaming and evaluation framework. Test for jailbreaks, prompt injection, and other vulnerabilities with adversarial attacks (PAIR, tree-of-attacks, crescendo). CI/CD integration. |  |
| 🔧 LLaMator | Framework for testing vulnerabilities of large language models with support for Russian language | |
| 🔧 Spikee | Comprehensive testing framework for LLM applications. Tests prompt injection, jailbreaks, and other vulnerabilities. Supports custom targets, attacks, judges, and guardrail evaluation |  |
| 🛡️ LocalMod | Self-hosted content moderation API with prompt injection detection, toxicity filtering, PII detection, and NSFW filtering. Runs 100% offline. |  |
Defensive mechanisms, guardrails, and security controls for protecting LLM applications.
| Category | Method / Technology | Principle of Operation (Mechanism) | Examples of Use / Developers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Fundamental Alignment | RLHF (Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback) | Training a model with reinforcement learning based on a reward model, which is trained on human evaluations. It optimizes for "usefulness" and "safety." | OpenAI (GPT-4), Yandex (YandexGPT) |
| DPO (Direct Preference Optimization) | Direct optimization of response probabilities based on preference pairs, bypassing the creation of a separate reward model. It is described as more stable and effective. | Meta (Llama 3), Mistral, open models | |
| Constitutional AI / RLAIF | Using the model itself to criticize and correct its responses according to a set of rules ("Constitution"). AI replaces human labeling (RLAIF). | Anthropic (Claude 3) | |
| 2. Internal Control (Interpretability) | Representation Engineering (RepE) | Detection and suppression of neuron activation vectors responsible for undesirable concepts (e.g., falsehood, lust for power) in real-time. | Center for AI Safety (CAIS) |
| Circuit Breakers | Redirection ("short-circuiting") of internal representations of malicious queries into orthogonal space, causing failure or nonsense. | GraySwan AI, researchers | |
| Machine Unlearning | Algorithmic "erasure" of dangerous knowledge or protected data from model weights (e.g., via Gradient Ascent) so that the model physically "forgets" them. | Research groups, Microsoft | |
| 3. External Filters (Guardrails) | Llama Guard | A specialized LLM-classifier that checks incoming prompts and outgoing responses for compliance with a risk taxonomy (MLCommons). | Meta |
| NeMo Guardrails | A programmable dialogue management system. It uses the Colang language for strict topic adherence and attack blocking. | NVIDIA | |
| Prompt Guard / Shields | Lightweight models (based on BERT/DeBERTA) for detecting jailbreaks and prompt injections before they reach the LLM. | Meta, Azure AI | |
| SmoothLLM | A randomized smoothing method: creating copies of a prompt with symbolic perturbations to disrupt the structure of adversarial attacks (e.g., GCG suffixes). | Researchers (SmoothLLM authors) | |
| Google Safety Filters | Multi-level content filtering with customizable sensitivity thresholds and semantic vector analysis. | Google (Gemini API) | |
| 4. System Instructions | System Prompts / Tags | Using special tokens (e.g., </start_header_id>) to separate system and user instructions. |
OpenAI, Meta, Anthropic |
| Instruction Hierarchy | Prioritizing system instructions over user instructions to protect against prompt injection, especially when the model learns to ignore "forget past instructions" commands. | OpenAI (GPT-4o Mini) | |
| 5. Testing (Red Teaming) | Automated Attacks (GCG, AutoDAN) | Using algorithms and other LLMs to generate hundreds of thousands of adversarial prompts to find vulnerabilities. | Research groups |
| Tool | Description | Stars |
|---|---|---|
| 🛡️ PurpleLlama | Set of tools to assess and improve LLM security. |  |
| 🛡️ Rebuff | API with built-in rules for identifying prompt injection and detecting data leakage through canary words. (ProtectAI is now part of Palo Alto Networks) |  |
| 🔒 LLM Guard | Self-hostable tool with multiple prompt and output scanners for various security issues. |  |
| 🚧 NeMo Guardrails | Tool that protects against jailbreak and hallucinations with customizable rulesets. |  |
| 👁️ Vigil | Offers dockerized and local setup options, using proprietary HuggingFace datasets for security detection. |  |
| 🧰 LangKit | Provides functions for jailbreak detection, prompt injection, and sensitive information detection. |  |
| 🛠️ GuardRails AI | Focuses on functionality, detects presence of secrets in responses. |  |
| 🦸 Hyperion Alpha | Detects prompt injections and jailbreaks. | N/A |
| 🛡️ LLM-Guard | Tool for securing LLM interactions. (ProtectAI is now part of Palo Alto Networks) |  |
| 🚨 Whistleblower | Tool for detecting and preventing LLM vulnerabilities. |  |
| 🔍 Plexiglass | Security tool for LLM applications. |  |
| 🔍 Prompt Injection defenses | Rules for protected LLM |  |
| 🔍 LLM Data Protector | Tools for protected LLM in chatbots | N/A |
| 🔍 Gen AI & LLM Security for developers: Prompt attack mitigations on Gemini | Security tool for LLM applications. |  |
| 🔍 TrustGate | Generative Application Firewall that detects and blocks attacks against GenAI Applications. |  |
| 🛡️ Tenuo | Capability tokens for AI agents with task-scoped TTLs, offline verification and proof-of-possession binding. | ) |
| 🛡️ AIDEFEND | Practical knowledge base for AI security defenses. Based on MAESTRO framework, MITRE D3FEND, ATLAS, ATT&CK, Google Secure AI Framework, and OWASP Top 10 LLM 2025/ML Security 2023. | N/A |
Frameworks and methodologies for identifying and modeling threats in LLM systems.
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Secure LLM Deployment: Navigating and Mitigating Safety Risks | Research paper on LLM security [sorry, but is really cool] |
| ThreatModels | Repository for LLM threat models |
| Threat Modeling LLMs | AI Village resource on threat modeling for LLMs |
| Sberbank AI Cybersecurity Threat Model | Sberbank's threat model for AI cybersecurity |
| Pangea Attack Taxonomy | Comprehensive taxonomy of AI/LLM attacks and vulnerabilities |
Tools and platforms for monitoring LLM applications, detecting anomalies, and tracking security events.
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Langfuse | Open Source LLM Engineering Platform with security capabilities. |
| HiveTrace | LLM monitoring and security platform for GenAI applications. Detects prompt injection, jailbreaks, malicious HTML/Markdown elements, and PII. Provides real-time anomaly detection and security alerts. |
Tools and techniques for watermarking LLM-generated content to detect AI-generated text.
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| MarkLLM | An Open-Source Toolkit for LLM Watermarking. |
Resources, databases, and benchmarks for understanding and testing jailbreak techniques against LLMs.
| Resource | Description | Stars |
|---|---|---|
| JailbreakBench | Website dedicated to evaluating and analyzing jailbreak methods for language models | N/A |
| L1B3RT45 | GitHub repository containing information and tools related to AI jailbreaking |  |
| llm-hacking-database | This repository contains various attacks against Large Language Models |  |
| HaizeLabs jailbreak Database | This database contains jailbreaks for multimodal language models | N/A |
| Lakera PINT Benchmark | A comprehensive benchmark for prompt injection detection systems. Evaluates detection systems across multiple categories (prompt injection, jailbreak, hard negatives, chat, documents) and supports evaluation in 20+ languages. Open-source benchmark with Jupyter notebook for custom evaluations. |  |
| EasyJailbreak | An easy-to-use Python framework to generate adversarial jailbreak prompts |  |
Resources for understanding and interpreting LLM behavior, decision-making, and internal mechanisms.
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Интерпретируемость LLM | Dmitry Kolodezev's web page, which provides useful resources with LLM interpretation techniques |
Prompt Injection Test (PINT) benchmark scores comparing different prompt injection detection systems.
| Name | PINT Score | Test Date |
|---|---|---|
| Lakera Guard | 95.2200% | 2025-05-02 |
| Azure AI Prompt Shield for Documents | 89.1241% | 2025-05-02 |
| protectai/deberta-v3-base-prompt-injection-v2 | 79.1366% | 2025-05-02 |
| Llama Prompt Guard 2 (86M) | 78.7578% | 2025-05-05 |
| Google Model Armor | 70.0664% | 2025-08-27 |
| Aporia Guardrails | 66.4373% | 2025-05-02 |
| Llama Prompt Guard | 61.8168% | 2025-05-02 |
Note: ProtectAI is now part of Palo Alto Networks
Note: For the complete and most up-to-date interactive leaderboard, visit the Hugging Face leaderboard or the GitHub repository.
From this repo (last updated: December 18, 2025)
This is a Safety Benchmark from Stanford University
Security considerations, attacks, and defenses for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems.
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Security Risks in RAG | Article on security risks in Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) |
| How RAG Poisoning Made LLaMA3 Racist | Blog post about RAG poisoning and its effects on LLaMA3 |
| Adversarial AI - RAG Attacks and Mitigations | GitHub repository on RAG attacks, mitigations, and defense strategies |
| PoisonedRAG | GitHub repository about poisoned RAG systems |
| ConfusedPilot: Compromising Enterprise Information Integrity and Confidentiality with Copilot for Microsoft 365 | Article about RAG vulnerabilities |
| Awesome Jailbreak on LLMs - RAG Attacks | Collection of RAG-based LLM attack techniques |
Security tools, benchmarks, and research focused on autonomous AI agents and their vulnerabilities.
| Tool | Description | Stars |
|---|---|---|
| invariant | A trace analysis tool for AI agents. |  |
| AgentBench | A Comprehensive Benchmark to Evaluate LLMs as Agents (ICLR'24) |  |
| Agent Hijacking, the true impact of prompt injection | Guide for attack langchain agents | Article |
| Breaking Agents: Compromising Autonomous LLM Agents Through Malfunction Amplification | Research about typical agent vulnerabilities | Article |
| Model Context Protocol (MCP) at First Glance: Studying the Security and Maintainability of MCP Servers | First large-scale empirical study of MCP servers security and maintainability | Article |
| Awesome MCP Security | Curated list of MCP security resources |  |
| Awesome LLM Agent Security | Comprehensive collection of LLM agent security resources, attacks, vulnerabilities |  |
| MCP Security Analysis | Research paper on MCP security vulnerabilities and analysis | Article |
| Tenuo | Capability-based authorization framework for AI agents. Task-scoped warrants with cryptographic attenuation, PoP binding, offline verification. LangChain/LangGraph/MCP integrations. |  |
Security research and analysis of AI-powered browser agents and their unique attack vectors.
| Resource | Description | Source |
|---|---|---|
| From Inbox to Wipeout: Perplexity Comet's AI Browser Quietly Erasing Google Drive | Research on zero-click Google Drive wiper attack via Perplexity Comet. Shows how polite, well-structured emails can trigger destructive actions in agentic browsers. | Straiker STAR Labs |
| Agentic Browser Security Analysis | Research paper on security vulnerabilities in agentic browsers | Article |
| Browser AI Agents: The New Weakest Link | Analysis of security risks in browser-based AI agents | Sqrx Labs |
| Comet Prompt Injection Vulnerability | Brave's analysis of prompt injection vulnerabilities in Perplexity Comet browser | Brave |
Proof of Concept implementations demonstrating various LLM attacks, vulnerabilities, and security research.
| Tool | Description | Stars |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Adversarial Examples | Jailbreaking Large Language Models with Visual Adversarial Examples |  |
| Weak-to-Strong Generalization | Weak-to-Strong Generalization: Eliciting Strong Capabilities With Weak Supervision |  |
| Image Hijacks | Repository for image-based hijacks of large language models |  |
| CipherChat | Secure communication tool for large language models |  |
| LLMs Finetuning Safety | Safety measures for fine-tuning large language models |  |
| Virtual Prompt Injection | Tool for virtual prompt injection in language models |  |
| FigStep | Jailbreaking Large Vision-language Models via Typographic Visual Prompts |  |
| stealing-part-lm-supplementary | Some code for "Stealing Part of a Production Language Model" |  |
| Hallucination-Attack | Attack to induce LLMs within hallucinations |  |
| llm-hallucination-survey | Reading list of hallucination in LLMs. Check out our new survey paper: "Siren's Song in the AI Ocean: A Survey on Hallucination in Large Language Models" |  |
| LMSanitator | LMSanitator: Defending Large Language Models Against Stealthy Prompt Injection Attacks |  |
| Imperio | Imperio: Robust Prompt Engineering for Anchoring Large Language Models |  |
| Backdoor Attacks on Fine-tuned LLaMA | Backdoor Attacks on Fine-tuned LLaMA Models |  |
| CBA | Consciousness-Based Authentication for LLM Security |  |
| MuScleLoRA | A Framework for Multi-scenario Backdoor Fine-tuning of LLMs |  |
| BadActs | BadActs: Backdoor Attacks against Large Language Models via Activation Steering |  |
| TrojText | Trojan Attacks on Text Classifiers |  |
| AnyDoor | Create Arbitrary Backdoor Instances in Language Models |  |
| PromptWare | A Jailbroken GenAI Model Can Cause Real Harm: GenAI-powered Applications are Vulnerable to PromptWares |  |
| BrokenHill | Automated attack tool that generates crafted prompts to bypass restrictions in LLMs using greedy coordinate gradient (GCG) attack |  |
| OWASP Agentic AI | OWASP Top 10 for Agentic AI (AI Agent Security) - Pre-release version |  |
Educational platforms, CTF challenges, courses, and training resources for learning LLM security.
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Gandalf | Interactive LLM security challenge game |
| Prompt Airlines | Platform for learning and practicing prompt engineering |
| PortSwigger LLM Attacks | Educational resource on WEB LLM security vulnerabilities and attacks |
| Invariant Labs CTF 2024 | CTF. You should hack LLM agentic |
| Invariant Labs CTF Summer 24 | Hugging Face Space with CTF challenges |
| Crucible | LLM security training platform |
| Poll Vault CTF | CTF challenge with ML/LLM components |
| MyLLMDoc | LLM security training platform |
| AI CTF PHDFest2 2025 | AI CTF competition from PHDFest2 2025 |
| AI in Security | Russian platform for AI security training |
| DeepLearning.AI Red Teaming Course | Short course on red teaming LLM applications |
| Learn Prompting: Offensive Measures | Guide on offensive prompt engineering techniques |
| Application Security LLM Testing | Free LLM security testing |
| Salt Security Blog: ChatGPT Extensions Vulnerabilities | Article on security flaws in ChatGPT browser extensions |
| safeguarding-llms | TMLS 2024 Workshop: A Practitioner's Guide To Safeguarding Your LLM Applications |
| Damn Vulnerable LLM Agent | Intentionally vulnerable LLM agent for security testing and education |
| GPT Agents Arena | Platform for testing and evaluating LLM agents in various scenarios |
| AI Battle | Interactive game focusing on AI security challenges |
| AI/LLM Exploitation Challenges | Challenges to test your knowledge of AI, ML, and LLMs |
| TryHackMe AI/ML Security Threats | Walkthrough and writeup for TryHackMe AI/ML Security Threats room |
Research articles, security advisories, and technical papers from the security community.
| Title | Authors | Year |
|---|---|---|
| 📄 Bypassing Meta's LLaMA Classifier: A Simple Jailbreak | Robust Intelligence | 2024 |
| 📄 Vulnerabilities in LangChain Gen AI | Unit42 | 2024 |
| 📄 Detecting Prompt Injection: BERT-based Classifier | WithSecure Labs | 2024 |
| 📄 Practical LLM Security: Takeaways From a Year in the Trenches | NVIDIA | 2024 |
| 📄 Security ProbLLMs in xAI's Grok | Embrace The Red | 2024 |
| 📄 Persistent Pre-Training Poisoning of LLMs | SpyLab AI | 2024 |
| 📄 Navigating the Risks: A Survey of Security, Privacy, and Ethics Threats in LLM-Based Agents | Multiple Authors | 2024 |
| 📄 Practical AI Agent Security | Meta | 2025 |
| 📄 Security Advisory: Anthropic's Slack MCP Server Vulnerable to Data Exfiltration | Embrace The Red | 2025 |
Step-by-step guides and tutorials for understanding and implementing LLM security practices.
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| 📚 HADESS - Web LLM Attacks | Understanding how to carry out web attacks using LLM |
| 📚 Red Teaming with LLMs | Practical methods for attacking AI systems |
| 📚 Lakera LLM Security | Overview of attacks on LLM |
Comprehensive books covering LLM security, adversarial AI, and secure AI development practices.
| 📖 Title | 🖋️ Author(s) | 🔍 Description |
|---|---|---|
| The Developer's Playbook for Large Language Model Security | Steve Wilson | 🛡️ Comprehensive guide for developers on securing LLMs |
| Generative AI Security: Theories and Practices (Future of Business and Finance) | Ken Huang, Yang Wang, Ben Goertzel, Yale Li, Sean Wright, Jyoti Ponnapalli | 🔬 In-depth exploration of security theories, laws, terms and practices in Generative AI |
| Adversarial AI Attacks, Mitigations, and Defense Strategies: A cybersecurity professional's guide to AI attacks, threat modeling, and securing AI with MLSecOps | John Sotiropoulos | Practical examples of code for your best mlsecops pipeline |
Security blogs, Twitter feeds, and Telegram channels focused on AI/LLM security.
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Embrace The Red | Blog on AI security, red teaming, and LLM vulnerabilities |
| HiddenLayer | AI security company blog |
| CyberArk | Blog on AI agents, identity risks, and security |
| Straiker | AI security research and agentic browser security |
| Firetail | LLM security, prompt injection, and AI vulnerabilities |
| Palo Alto Networks | Unit 42 research on AI security and agentic AI attacks |
| Trail of Bits | Security research including AI/ML pickle file security |
| NCSC | UK National Cyber Security Centre blog on AI safeguards |
| Knostic | AI Security Posture Management (AISPM) |
| 0din | Secure LLM and RAG deployment practices |
| @llm_sec | Twitter feed on LLM security |
| @LLM_Top10 | Twitter feed on OWASP LLM Top 10 |
| @aivillage_dc | AI Village Twitter |
| @elder_plinius | Twitter feed on AI security |
| Channel | Language | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PWN AI | RU | Practical AI Security and MLSecOps: LLM security, agents, guardrails, real-world threats |
| Борис_ь с ml | RU | Machine Learning + Information Security: ML, data science and cyber/AI security |
| Евгений Кокуйкин — Raft | RU | Building Raft AI and GPT-based applications: trust & safety, reliability and security |
| LLM Security | RU | Focused on LLM security: jailbreaks, prompt injection, adversarial attacks, benchmarks |
| AISecHub | EN | Global AI security hub: curated research, articles, reports and tools |
| AI Security Lab | RU | Laboratory by Raft x ITMO University: breaking and defending AI systems |
| ML&Sec Feed | RU/EN | Aggregated feed for ML & security: news, tools, research links |
| AISec [x_feed] | RU/EN | Digest of AI security content from X, blogs and papers |
| AI SecOps | RU | AI Security Operations: monitoring, incident response, SIEM/SOC integrations |
| OK ML | RU | ML/DS/AI channel with focus on repositories, tools and vulnerabilities |
| AI Attacks | EN | Stream of AI attack examples and threat intelligence |
| AGI Security | EN | Artificial General Intelligence Security discussions |
Datasets for testing LLM security, prompt injection examples, and safety evaluation data.
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Safety and privacy with Large Language Models | GitHub repository on LLM safety and privacy |
| Jailbreak LLMs | Data for jailbreaking Large Language Models |
| ChatGPT System Prompt | Repository containing ChatGPT system prompts |
| Do Not Answer | Project related to LLM response control |
| ToxiGen | Microsoft dataset |
| SafetyPrompts | A Living Catalogue of Open Datasets for LLM Safety |
| llm-security-prompt-injection | This project investigates the security of large language models by performing binary classification of a set of input prompts to discover malicious prompts. Several approaches have been analyzed using classical ML algorithms, a trained LLM model, and a fine-tuned LLM model. |
| Prompt Injections Dataset | Dataset containing prompt injection examples for testing and research |
Operational security considerations: supply chain risks, infrastructure vulnerabilities, and production deployment security.
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| https://sysdig.com/blog/llmjacking-stolen-cloud-credentials-used-in-new-ai-attack/ | LLMJacking: Stolen Cloud Credentials Used in New AI Attack |
| https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/security | Hugging Face Hub Security Documentation |
| https://github.com/ShenaoW/awesome-llm-supply-chain-security | LLM Supply chain security resources |
| https://developer.nvidia.com/blog/secure-llm-tokenizers-to-maintain-application-integrity/ | Secure LLM Tokenizers to Maintain Application Integrity |
| https://sightline.protectai.com/ | Sightline by ProtectAI (ProtectAI is now part of Palo Alto Networks) Check vulnerabilities on: • Nemo by Nvidia • Deep Lake • Fine-Tuner AI • Snorkel AI • Zen ML • Lamini AI • Comet • Titan ML • Deepset AI • Valohai For finding LLMops tools vulnerabilities |
| ShadowMQ: How Code Reuse Spread Critical Vulnerabilities Across the AI Ecosystem | Research on critical RCE vulnerabilities in AI inference servers (Meta Llama Stack, NVIDIA TensorRT-LLM, vLLM, SGLang, Modular) caused by unsafe ZeroMQ and pickle deserialization |
Comprehensive security frameworks, standards, and governance models for LLM and AI security.
 OWASP Top 10 for LLM Applications 2025 (v2.0) Updated list including System Prompt Leakage, Vector and Embedding Weaknesses |
 OWASP Top 10 for Agentic Applications (2026 Edition) First industry standard for autonomous AI agent risks (released Dec 2025) |
 OWASP AI Testing Guide v1 Open standard for testing AI system trustworthiness (Nov 2025) |
 GenAI Security Solutions Reference Guide Vendor-neutral guide for GenAI security architecture (Q2-Q3 2025) |
 LLM AI Cybersecurity & Governance Checklist Security and governance checklist |
 LLMSecOps Cybersecurity Solution Landscape Solution landscape overview |
All OWASP GenAI Resources: genai.owasp.org/resources/
LLMSECOPS, by OWASP
| Framework | Organization | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MCP Security Governance | Cloud Security Alliance | Governance framework for the Model Context Protocol ecosystem. Developing policies, standards, and assessment tools for secure MCP server deployment. |
| Databricks AI Security Framework (DASF) 2.0 | Databricks | Actionable framework for managing AI security. Includes 62 security risks across three stages and 64 controls applicable to any data and AI platform. |
| Google Secure AI Framework (SAIF) 2.0 | Secure AI Framework focused on agents. Practitioner-focused framework for building powerful agents users can trust. | |
| Snowflake AI Security Framework | Snowflake | Comprehensive framework for securing AI deployments on Snowflake platform. |
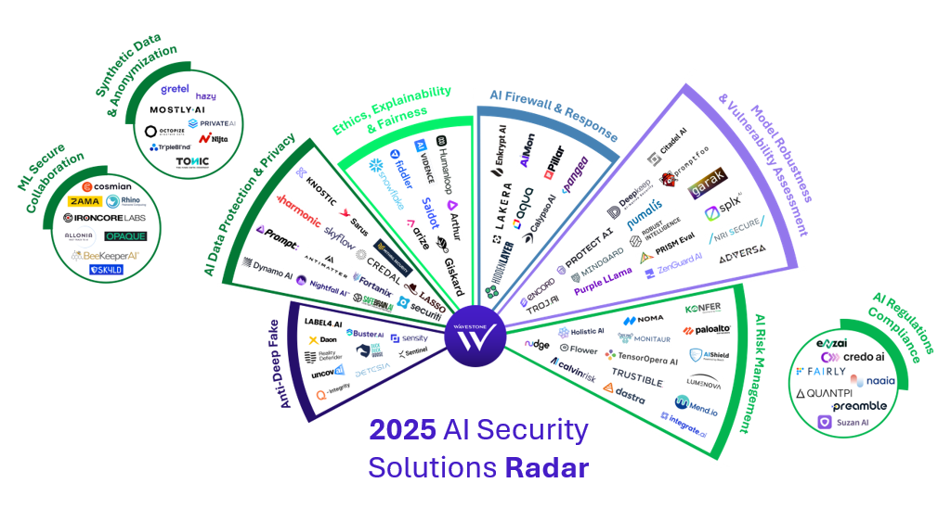
Source: 2025 AI Security Solutions Radar by RiskInsight-Wavestone
Community resources, platforms, and collaborative spaces for LLM security practitioners.
| Platform | Details |
|---|---|
| OWASP SLACK | Channels: • #project-top10-for-llm • #ml-risk-top5 • #project-ai-community • #project-mlsec-top10 • #team-llm_ai-secgov • #team-llm-redteam • #team-llm-v2-brainstorm |
| Awesome LLM Security | GitHub repository |
| Awesome AI Security Telegram | Curated list of Telegram channels and chats on AI Security, AI/MLSecOps, LLM Security |
| LVE_Project | Official website |
| Lakera AI Security resource hub | Google Sheets document |
| llm-testing-findings | Templates with recommendations, CWE and other |
| Arcanum Prompt Injection Taxonomy | Structured taxonomy of prompt injection attacks categorizing attack intents, techniques, and evasions. Resource for security researchers, AI developers, and red teamers. |
Security benchmarks, evaluation frameworks, and standardized tests for assessing LLM security capabilities.
| Resource | Description | Stars |
|---|---|---|
| Backbone Breaker Benchmark (b3) | Human-grounded benchmark for testing AI agent security. Built by Lakera with UK AI Security Institute using 194,000+ human attack attempts from Gandalf: Agent Breaker. Tests backbone LLM resilience across 10 threat snapshots. | Article |
| Backbone Breaker Benchmark Paper | Research paper on the Backbone Breaker Benchmark methodology and findings | Article |
| CyberSoCEval | Meta's benchmark for evaluating LLM capabilities in malware analysis and threat intelligence reasoning | Meta Research |
| Agent Security Bench (ASB) | Benchmark for agent security |  |
| AI Safety Benchmark | Comprehensive benchmark for AI safety evaluation | N/A |
| AI Safety Benchmark Paper | Research paper on AI safety benchmarking methodologies | Article |
| Evaluating Prompt Injection Datasets | Analysis and evaluation framework for prompt injection datasets | HiddenLayer |
| LLM Security Guidance Benchmarks | Benchmarking lightweight, open-source LLMs for security guidance effectiveness using SECURE dataset |  |
| SECURE | Benchmark for evaluating LLMs in cybersecurity scenarios, focusing on Industrial Control Systems |  |
| NIST AI TEVV | AI Test, Evaluation, Validation and Verification framework by NIST | N/A |
| Taming the Beast: Inside the Llama 3 Red Teaming Process | DEF CON 32 presentation on Llama 3 red teaming | 2024 |