Note: All code was written with the help of Claude.
As a programming beginner, I could never have done it alone 😢
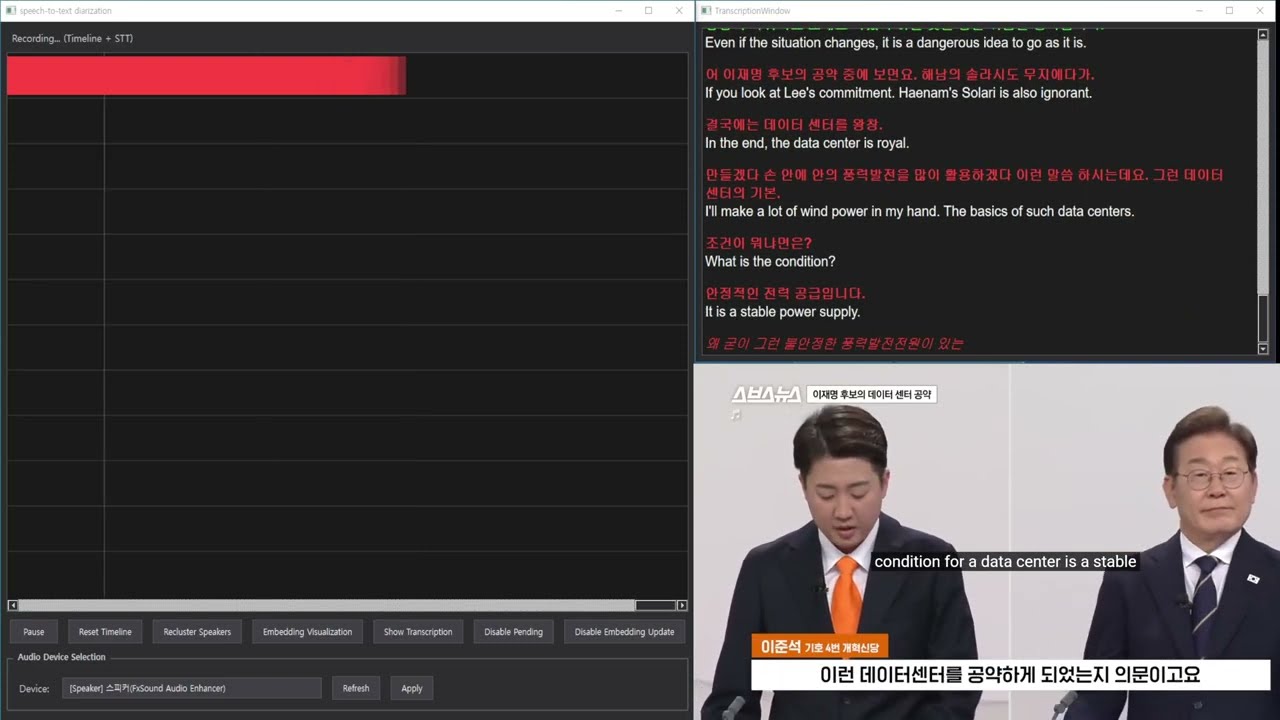
Utterr is a real-time speaker diarization system that implements highly accurate speaker identification using straightforward, intuitive logic. The system captures audio in real-time, identifies different speakers, and visualizes the results on an interactive timeline.
This project demonstrates how to build a practical speaker diarization pipeline using modern deep learning models without complex implementations.
-
Real-time Audio Capture: Leverages the
SoundCardlibrary to capture microphone or system audio (loopback) in real-time. Unlike PyAudio, SoundCard can capture speaker output via loopback without additional setup on Windows. -
Voice Activity Detection (VAD): Uses Silero VAD for accurate speech segment detection in audio streams.
-
Speaker Embedding Extraction: Extracts speaker embeddings (voice feature vectors) using pre-trained models:
- SpeechBrain's ECAPA-TDNN (rt_timeline.py)
- WeSpeaker ResNet34-LM via pyannote.audio (rt_timeline_pyannote.py) - Best Accurate
-
Intelligent Speaker Clustering: Novel approach with two-stage speaker identification:
- New speakers are initially classified as 'Pending'
- Automatic clustering promotes pending speakers once sufficient data is accumulated
- Uses intuitive cosine similarity-based classification
-
Manual Reclustering: Correct clustering errors by manually reassigning all accumulated embeddings to a specified number of speakers.
-
Real-time Timeline Visualization: PyQt6-based interactive timeline showing speaker activity in real-time.
-
Embedding Distribution Visualization: 2D PCA visualization of high-dimensional speaker embeddings.
These versions display real-time speaker timelines without text transcription:
| File | Embedding Model | Accuracy | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
rt_timeline.py |
SpeechBrain ECAPA-TDNN | Good | Original implementation |
rt_timeline_pyannote.py |
WeSpeaker ResNet34-LM | Better | Recommended - More accurate speaker identification |
| File | Requirements | Description |
|---|---|---|
speech-to-text diarization.py |
Azure Speech SDK API Key | Provides word-level timestamps with speaker attribution. Uses Azure Speech SDK to obtain precise word-level timestamps, enabling display of which speaker said each word. |
- Operating System: Windows (SoundCard's loopback functionality only works on Windows)
- Python: 3.10 or higher
- Conda: Recommended for environment management
-
Create and activate Conda environment
conda create -n rtt_env python=3.10 conda activate rtt_env
-
Install required packages
It's recommended to install PyTorch according to your system environment (CUDA support).
- CPU version:
pip install torch torchaudio soundcard numpy PyQt6 scikit-learn matplotlib speechbrain azure-cognitiveservices-speech
- GPU (CUDA) version: (if you have NVIDIA GPU) Check the installation command for your CUDA version on the PyTorch official website.
- CPU version:
Run the program with administrator privileges (required on first launch):
# For timeline-only (recommended)
python rt_timeline_pyannote.py
# Or original version
python rt_timeline.py
# Or with speech-to-text
python speech-to-text diarization.py- When the program starts, it will automatically download the required models
- Wait for the status message: "Ready - Press Start button to begin"
- (Optional) Select your audio input device:
- Choose between microphone or speaker (loopback) input
- Click "Refresh" to update the device list
- Click "Apply" to confirm your selection
- Click "Start" to begin real-time speaker diarization
- Start/Pause: Begin or pause recording
- Reset Timeline: Clear the timeline and start fresh
- Recluster Speakers: Manually reassign all embeddings to a specified number of speakers
- Embedding Visualization: View 2D PCA projection of speaker embeddings
- Disable/Enable Pending: Toggle the pending speaker queue
- Disable/Enable Embedding Update: Toggle dynamic speaker profile updates
The system uses a straightforward, intuitive approach to achieve high-accuracy real-time speaker diarization:
- Processes audio in 1-second windows (
WINDOW_SIZE) - New windows created every 0.1 seconds (
WINDOW_PROCESS_INTERVAL) - Overlapping windows ensure no speech is missed
- Each window passes through Silero VAD model
- Distinguishes speech from non-speech segments
- Only speech segments proceed to embedding extraction
- Speech windows converted to high-dimensional embeddings
- Embeddings capture unique voice characteristics
- Models used:
- SpeechBrain's ECAPA-TDNN (192-dim)
- pyannote.audio's WeSpeaker ResNet34-LM (256-dim, more accurate)
- New speakers with low similarity to existing speakers enter "Pending" queue
- Threshold:
PENDING_THRESHOLD(default 0.3) - Prevents premature speaker assignment
- Allows accumulation of data for reliable clustering
- When pending queue reaches
MIN_CLUSTER_SIZEembeddings - Agglomerative Clustering identifies cohesive groups:
clustering = AgglomerativeClustering( n_clusters=None, distance_threshold=AUTO_CLUSTER_DISTANCE_THRESHOLD, # 0.6 metric='cosine', linkage='average' )
- Largest cohesive cluster promoted as new speaker
- Hierarchical clustering well-suited for spherical speaker clusters
- Uses cosine similarity for speaker assignment
- Compares new embedding with representative embeddings (medians)
- Assignment process:
- Normalize embedding vectors
- Calculate similarities with all known speakers
- Assign to speaker with highest similarity (if above threshold)
- Update speaker profile if similarity exceeds
EMBEDDING_UPDATE_THRESHOLD
# Simplified classification logic
emb_norm = emb / np.linalg.norm(emb)
similarities = np.dot(mean_embs_norm, emb_norm)
best_speaker = active_speakers[np.argmax(similarities)]- User-triggered complete re-clustering
- Specify exact number of speakers
- Re-processes all collected embeddings
- Corrects automatic clustering errors
Key parameters (PENDING_THRESHOLD, AUTO_CLUSTER_DISTANCE_THRESHOLD) may require tuning based on:
- Environmental conditions
- Noise levels
- Number of speakers
- Voice similarity
Cosine similarity may struggle with:
- Speakers with very similar vocal timbres
- Simultaneous speech from similar voices
- Rapid speaker changes
- Lower thresholds: Better for similar voices, but may split single speakers
- Higher thresholds: Better for preventing splits, but may merge different speakers
- Solution: Use manual reclustering to correct post-hoc
This is a demonstration version with straightforward logic. While achieving good accuracy, it may not be perfectly robust in all exceptional situations. The simplicity of the approach is both its strength (easy to understand and modify) and limitation (may need adjustments for specific use cases).
| Parameter | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
PENDING_THRESHOLD |
0.3 | Similarity threshold for pending queue |
EMBEDDING_UPDATE_THRESHOLD |
0.4 | Threshold for updating speaker profiles |
AUTO_CLUSTER_DISTANCE_THRESHOLD |
0.6 | Distance threshold for auto-clustering |
MIN_CLUSTER_SIZE |
15 | Minimum embeddings for speaker promotion |
WINDOW_SIZE |
1.0s | Audio processing window duration |
- Use GPU: Significantly faster embedding extraction (CUDA recommended)
- Adjust thresholds: Fine-tune for your specific environment
- Monitor embedding visualization: Visual feedback helps understand clustering quality
- Use reclustering: Don't hesitate to manually correct mistakes
If you use this project or pyannote.audio, please cite:
@inproceedings{Plaquet23,
author={Alexis Plaquet and Hervé Bredin},
title={{Powerset multi-class cross entropy loss for neural speaker diarization}},
year=2023,
booktitle={Proc. INTERSPEECH 2023},
}
@inproceedings{Bredin23,
author={Hervé Bredin},
title={{pyannote.audio 2.1 speaker diarization pipeline: principle, benchmark, and recipe}},
year=2023,
booktitle={Proc. INTERSPEECH 2023},
}Contributions, issues, and feature requests are welcome! Feel free to check the issues page.
This project is open source and available under the MIT License.
Made with ❤️ and Claude AI