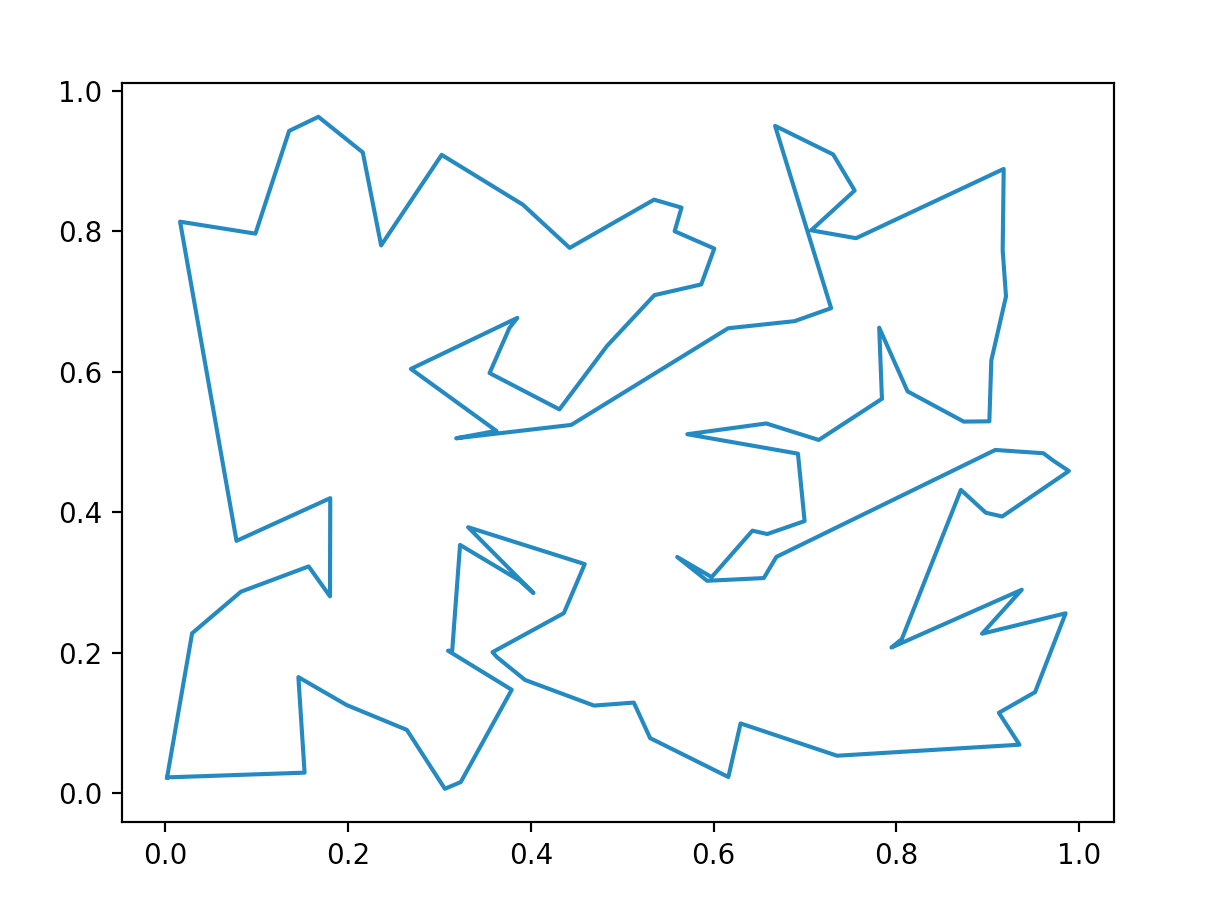
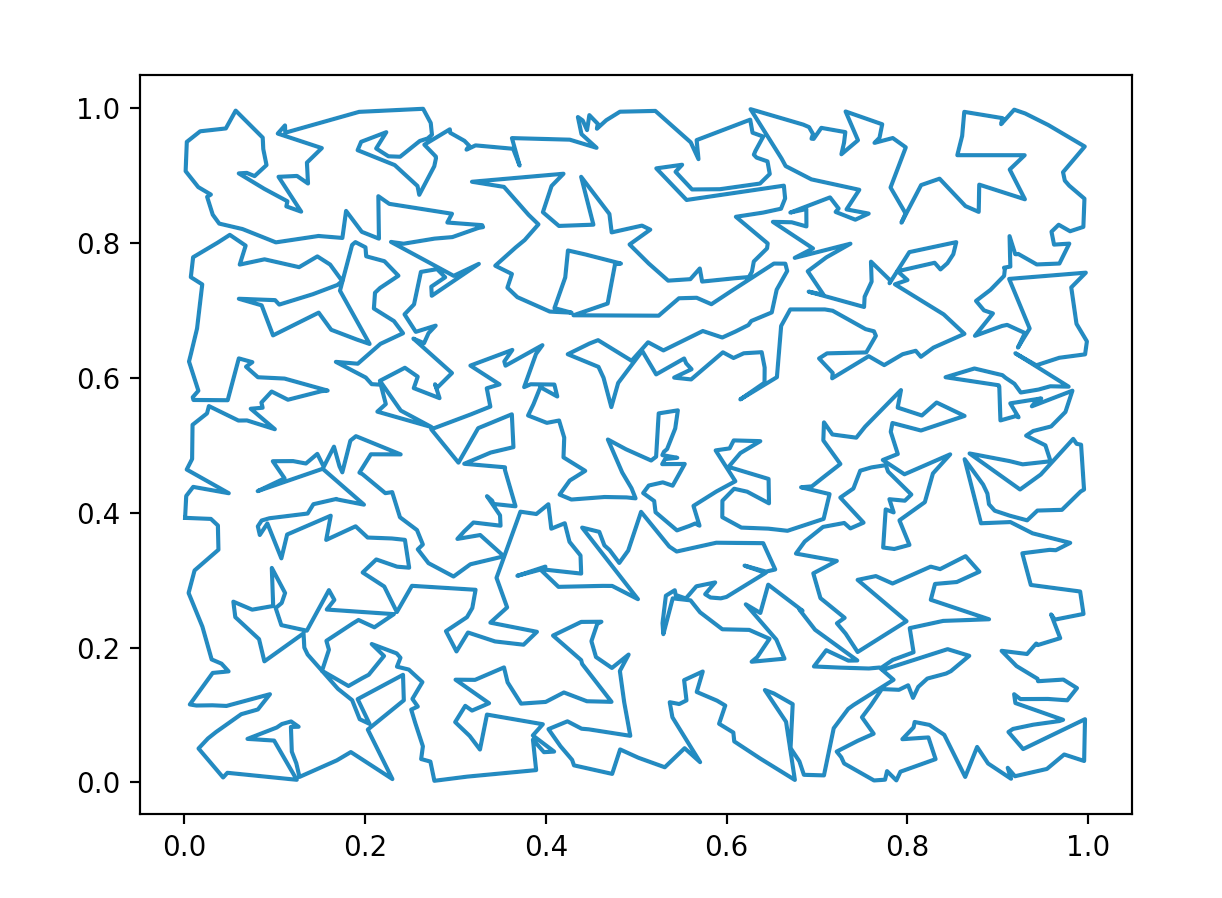
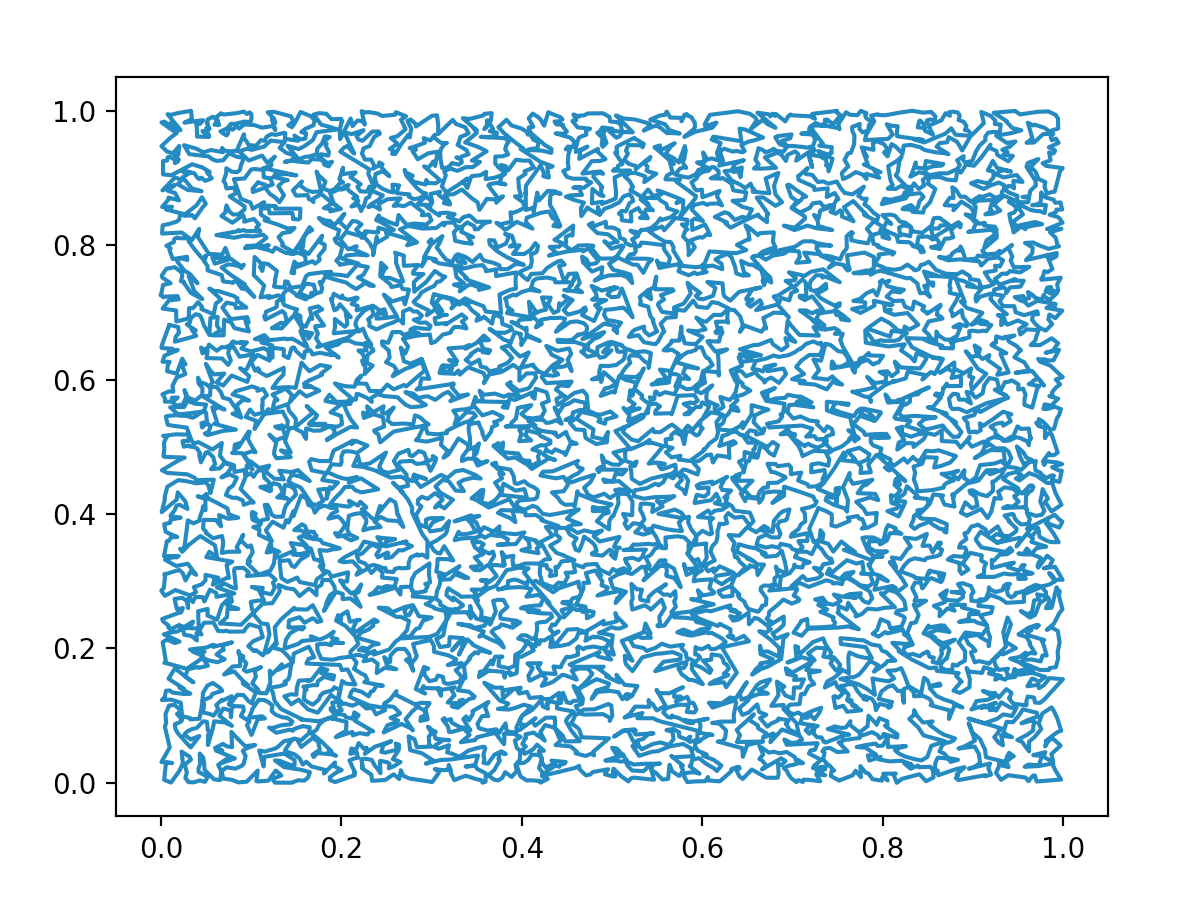
Various methods of generating random simple polygons have been proposed, with varying runtimes. In collaboration with one other Princeton student, I propose an algorithm that, given a positive integer input n, randomly generates n vertices within a confined rectangle on the 2D plane, calculates the convex hull of the vertex set, and iteratively connects the unconnected vertex and existing edge with the minimum distance until no more unconnected vertices remain. We present a naive approach with an O(n4) time complexity, and an improved approach using a minimum priority queue with O(n3) time complexity.
Our goal is to create polygons that are as "complicated" as possible—basically, the more winding and irregular the generated polygon is, the better. For larger and larger inputs, given some random point, it should become increasingly difficult to tell whether that point is inside or outside of the generated polygon. We find that this is indeed the case with our algorithm, especially for inputs greater than 10,000.
This project was developed in fulfillment of our final for Princeton University's COS 451: Computational Geometry Fall 2019 course. It is written in Python and uses Matplotlib for polygon visualization.
I developed the algorithm for our improved approach, and helped implement the Python code for both approaches. I also worked in conjuction with my partner to LaTeX the formal write-up.
- Clone the repo and cd into it:
git clone https://github.com/spoiledhua/random-simple-polygon-generation.git
cd random-simple-polygon-generation- Install Matplotlib:
pip3 install matplotlib- cd into the src file:
cd src-generate- Generate a random point set and answer the resulting prompt "Number of vertices: " with an integer n > 2. This will produce a test.txt file with all of the generated vertices:
python3 generate.py- To run the naive algorithm:
python3 main_naive.py- To run the improved algorithm:
python3 main_improved.pyOnce the algorithm terminates, a Matplotlib plot with the final polygon will display on a separate window. The terminal will display the number of vertices in the polygon and the execution time taken for the polygon generation.
To take a deeper look into our algorithm, implementation, and discussion, navigate to our formal write-up here.